________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
ENTRESTO is indicated in adult patients for the treatment of symptomatic chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. It is the first-in-class ARNI recommended for the treatment of chronic HFrEF and targets two essential pathways in a complementary manner.
To learn more, review the Summary of Product Characteristics.
Start with ENTRESTO® to see benefits and keep patients out of the hospital longer vs ACEi (enalapril)1–7
ENTRESTO as first choice keeps patients out of the hospital longer vs ACEi (enalapril)1,5,6
Regardless of where patients are in their journey, starting ENTRESTO as early as possible improves outcomes vs ACEi (enalapril).1,5,6
Start with ENTRESTO to maximise near and long-term benefits for your patients1,5,6
ENTRESTO is indicated in adult patients for the treatment of symptomatic chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.8
Discover the benefits of ENTRESTO vs ACEi (enalapril) in improving your chronic HFrEF patient’s treatment experience9,10
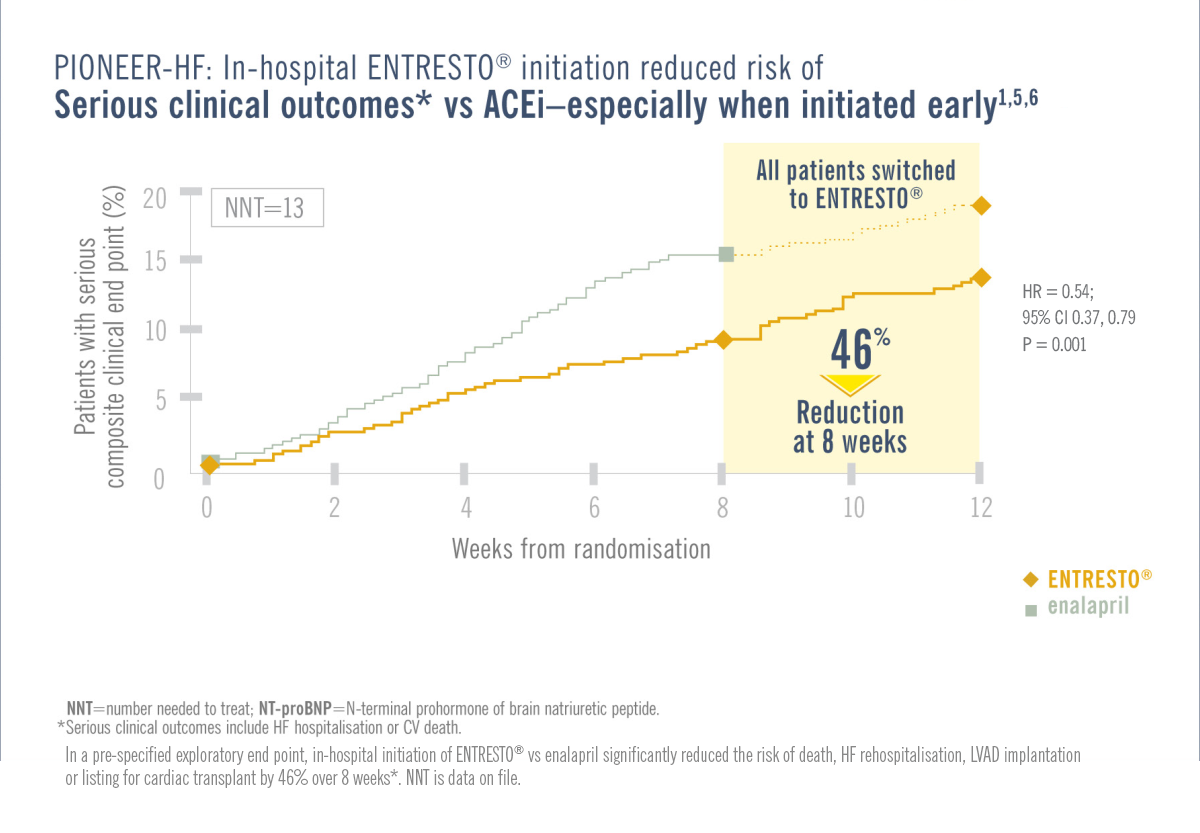
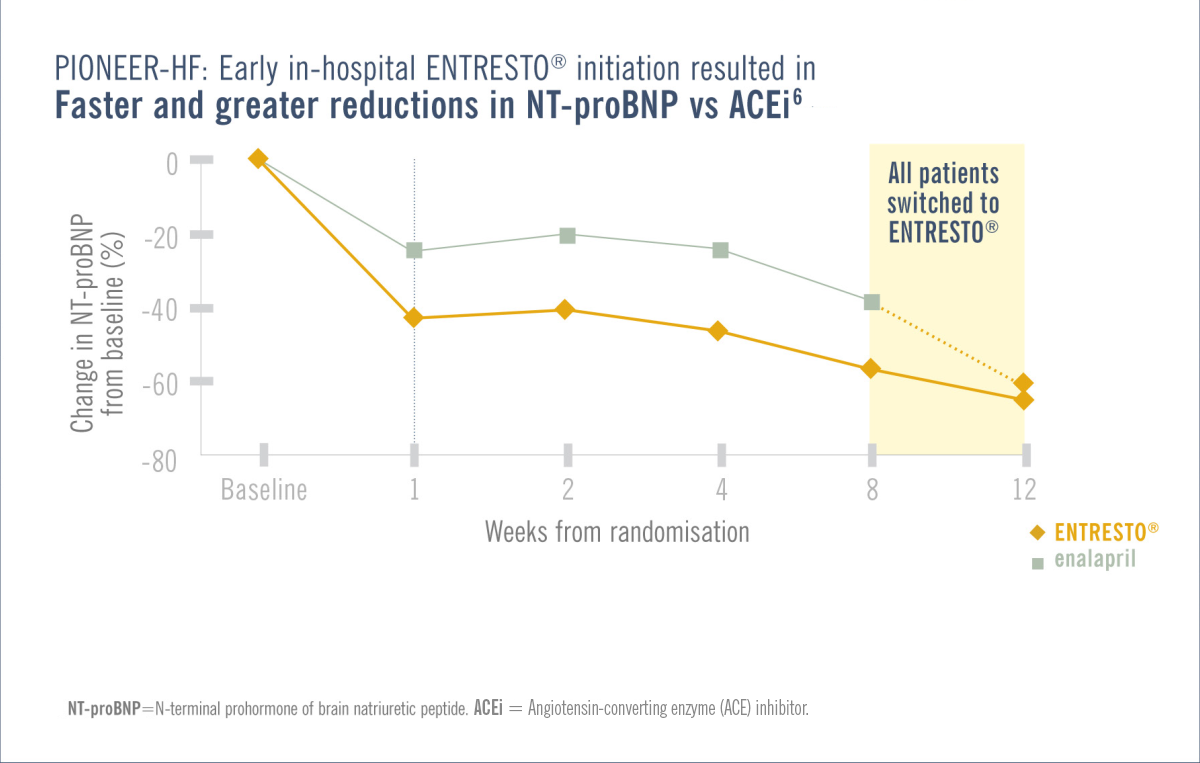
Patients in the PIONEER-HF/TRANSITION trial were required to be haemodynamically stabilised from an ADHF episode while in hospital.1,3
Starting ENTRESTO now reduces HF hospitalisations, saving hospital budgets and alleviating system burden11
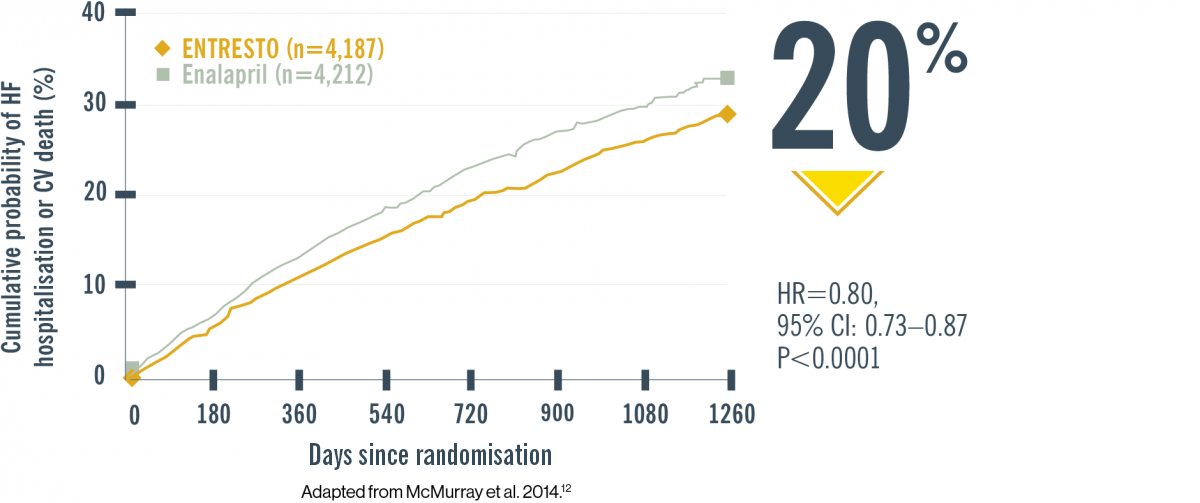
PARADIGM-HF (N=8,442): Lower risk of CV death or HF hospitalisation with ENTRESTO vs ACEi12
In a post hoc analysis, ENTRESTO reduced the relative risk of sudden cardiac death by 20% vs enalapril (P=0.0082)13
Discover the benefits of ENTRESTO vs ACEi (enalapril) in improving your chronic HFrEF patient’s treatment experience9,10
Contraindications:8
- Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients listed in the SmPC
- Concomitant use with ACEi. ENTRESTO should not be administered until 36 hours after discontinuing ACEi therapy
- Known history of angioedema related to previous ACEi or ARB therapy
- Hereditary or idiopathic angioedema
- Concomitant use with aliskiren-containing medicinal products in patients with diabetes mellitus or in patients with renal impairment (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73m2)
- Severe hepatic impairment, biliary cirrhosis and cholestasis
- Second and third trimesters of pregnancy
Special warnings and precautions for use8
Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
- The combination of ENTRESTO with an ACEi is contraindicated due to the increased risk of angioedema. ENTRESTO must not be initiated until 36 hours after taking the last dose of ACEi therapy. If treatment with ENTRESTO is stopped, ACEi therapy must not be initiated until 36 hours after the last dose of ENTRESTO
- The combination of ENTRESTO with direct renin inhibitors such as aliskiren is not recommended. The combination of ENTRESTO with aliskiren-containing products is contraindicated in patients with diabetes mellitus or in patients with renal impairment (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73m2)
- ENTRESTO contains valsartan, and therefore should not be co-administered with another ARB-containing product
Hypotension
- Treatment should not be initiated unless SBP is ≥100 mmHg. Patients with SBP <100 mmHg were not studied. Cases of symptomatic hypotension have been reported in patients treated with ENTRESTO during clinical studies, especially in patients ≥65 years old, patients with renal disease and patients with low SBP (<112 mmHg)
- When initiating therapy or during dose titration with ENTRESTO, blood pressure should be monitored routinely. If hypotension occurs, temporary down-titration or discontinuation of ENTRESTO is recommended. Dose adjustment of diuretics, concomitant antihypertensives and treatment of other causes of hypotension (e.g. hypovolaemia) should be considered
- Symptomatic hypotension is more likely to occur if the patient has been volume-depleted, e.g. by diuretic therapy, dietary salt restriction, diarrhoea or vomiting. Sodium and/or volume depletion should be corrected before starting treatment with ENTRESTO, however, such corrective action must be carefully weighed against the risk of volume overload
Impaired renal function
- Evaluation of patients with heart failure should always include assessment of renal function. Patients with mild and moderate renal impairment are more at risk of developing hypotension. There is very limited clinical experience in patients with severe renal impairment (estimated GFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2) and these patients may be at greatest risk of hypotension. There is no experience in patients with end-stage renal disease and use of ENTRESTO is not recommended
Worsening renal function
- Use of ENTRESTO may be associated with decreased renal function. The risk may be further increased by dehydration or concomitant use of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs). Down-titration should be considered in patients who develop a clinically significant decrease in renal function
Hyperkalaemia
- Treatment should not be initiated if the serum potassium level is >5.4 mmol/l. Use of ENTRESTO may be associated with an increased risk of hyperkalaemia, although hypokalaemia may also occur. Monitoring of serum potassium is recommended, especially in patients who have risk factors such as renal impairment, diabetes mellitus or hypoaldosteronism or who are on a high potassium diet or on mineralocorticoid antagonists. If patients experience clinically significant hyperkalaemia adjustment of concomitant medicinal products or temporary down–titration or discontinuation is recommended. If serum potassium level is >5.4 mmol/L, discontinuation should be considered
Angioedema
- Angioedema has been reported in patients treated with ENTRESTO. If angioedema occurs, ENTRESTO should be immediately discontinued and appropriate therapy and monitoring should be provided until complete and sustained resolution of signs and symptoms has occurred. It must not be re-administered. In cases of confirmed angioedema where swelling has been confined to the face and lips, the condition has generally resolved without treatment, although antihistamines have been useful in relieving symptoms
- Angioedema associated with laryngeal oedema may be fatal. Where there is involvement of the tongue, glottis or larynx likely to cause airway obstruction, appropriate therapy, e.g. adrenaline solution 1 mg/1 mL (0.3–0.5 mL), and/or measures necessary to ensure a patent airway, should be promptly administered
- Patients with a prior history of angioedema were not studied. As they may be at higher risk for angioedema, caution is recommended if ENTRESTO is used in these patients. ENTRESTO is contraindicated in patients with a known history of angioedema related to previous ACEi or ARB therapy or with hereditary or idiopathic angioedema
- Black patients have an increased susceptibility to develop angioedema
Patients with renal artery stenosis
- ENTRESTO may increase blood urea and serum creatinine levels in patients with bilateral or unilateral renal artery stenosis
- Caution is required in patients with renal artery stenosis and monitoring of renal function is recommended
Patients with NYHA functional classification IV
- Caution should be exercised when initiating ENTRESTO in patients with NYHA functional classification IV due to limited clinical experience in this population
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
- BNP is not a suitable biomarker of heart failure in patients treated with ENTRESTO because it is a neprilysin substrate
Patients with hepatic impairment
- There is limited clinical experience in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B classification) or with AST/ALT values more than twice the upper limit of the normal range. In these patients, exposure may be increased and safety is not established. Caution is therefore recommended when using it in these patients
- ENTRESTO is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment, biliary cirrhosis or cholestasis (Child-Pugh C classification)
Psychiatric disorders
- Psychiatric events such as hallucinations, paranoia and sleep disorders, in context of psychotic events, have been associated with ENTRESTO use. If a patient experiences such events, discontinuation of ENTRESTO treatment should be considered
ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARNI, angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor; CI, confidence interval; CV, cardiovascular;HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; HR, hazard ratio;LVAD, left ventricular assist device;NT-proBNP, N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide; NNT, number needed to treat; RR, risk reduction.
References:
- Velazquez EJ, et al. N Engl J Med 2019;380(6):539–548.
- Wachter R, et al. Eur J Heart Fail 2019;21(8):998–1007.
- Senni M, et al. Eur J Heart Fail 2019;22(2):303–312.
- Januzzi JL Jr, et al. JAMA 2019;322(11):1085–1095.
- DeVore AD, et al. Initiation of angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition after acute decompensated heart failure: results of the openlabel extension of the PIONEER-HF trial. Data presented at American College of Cardiology 68th Annual Scientific Session, March 2019.
- Morrow DA, et al. Circulation 2019;139(19):2285–2288.
- Maddox TM, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 2021;77:772–810.
- ENTRESTO Summary of Product Characteristics. www.medicines.ie
- Chandra A, et al. JAMA Cardiol 2018;3(6):498–505.
- Lewis EF, et al. Circ Heart Fail 2017;10(8):e003430.
- Gaziano TA, et al. JAMA Cardiol 2020;5(11):1236–1244.
- McMurray JJ, et al. N Engl J Med 2014;371:993–1004.
- Desai AS, et al. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(30).

